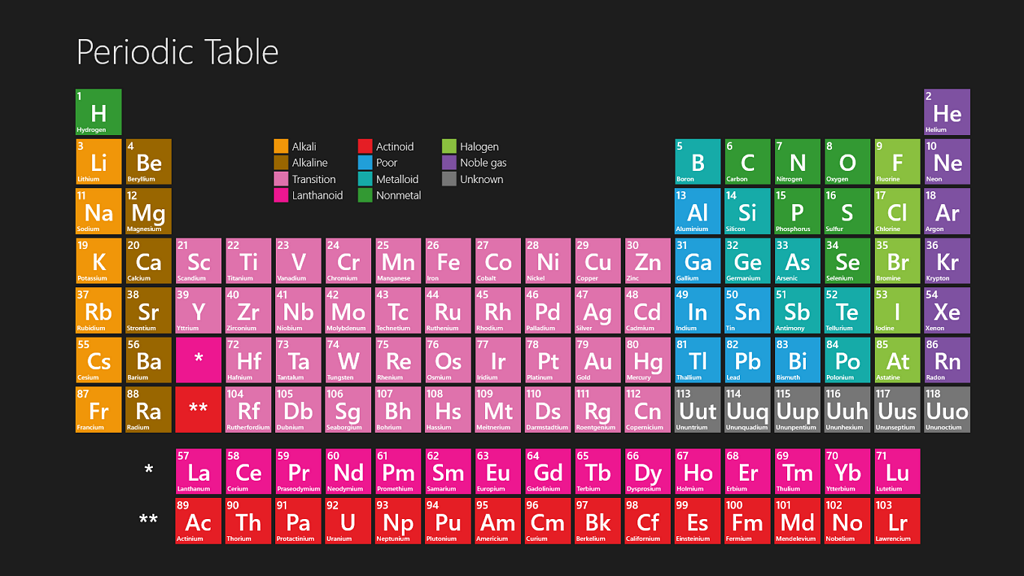
The periodic table of elements is a chart that contains information about every chemical element. The chart lists each element’s name, atomic number (the number of protons in an atom of the element), and symbol (an abbreviated form of the name).
Introduce the periodic table of elements
The periodic table of elements is a table that organizes all the known chemical elements in order of their atomic number. It was first developed by chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, and has been updated and revised over the years as new elements have been discovered.
The table is arranged so that each element is placed in one of eight groups based on similar characteristics. Some of the known elements are relatively abundant, while others exist only in trace amounts or were first discovered more recently.
Adjusted for inflation, $1.00 in 1869 is equivalent to $22.89 today. However, it can be difficult to measure monetary value across several decades due to inflation.
What are isotopes and why do they exist?
Isotopes are different versions of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The most common isotope is hydrogen-1 , which has no neutrons. Deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen, has one neutron, while tritium has two.
An atom’s number of protons determines what chemical element it represents. The number of neutrons determines the isotope. Isotopes are not separate elements, they are just variants of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
What are radioactive isotopes?
A radioactive isotope is an atom that is unstable and will break down over time by emitting radiation. Radioactive isotopes have a half-life, which is the amount of time it takes for half of the atoms to break down. Some isotopes are more radioactive than others.
Isotopes can be used for various purposes, including medical diagnosis and treatment, food preservation, and energy production.
What is an element’s atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons an atom has in its nucleus, which determines what element it represents. This number is the same as the number of electrons surrounding the atom’s nucleus.
How does a periodic table work for predicting chemical reactions?
A periodic table can be used to predict chemical reactions because it shows how the elements are related to each other.
If you know what elements are involved in a reaction, you can use the periodic table to figure out which atoms will be exchanging electrons and therefore creating a new compound. The periodic table can also help identify compounds that are already known.
Which of the following categories includes the majority of the elements?
A: metals
B: non-metals
C: metalloids
D: none of the above
(A) Metals. According to the Modern Version of the Periodic Table, “Metalloids and all elements in groups I-III except hydrogen are considered metals.” [Source] More info here . This includes the majority of elements on the table.
(B) Non-metals. According to the Modern Version of the Periodic Table, “Metalloids and all elements in groups IV-VI except carbon are considered nonmetals.” This includes most of the remaining elements on the table.
(C) Metalloids. According to the Modern Version of the Periodic Table, “Metalloids are elements that have some of the properties of metals and some of the properties of nonmetals.” This includes a small number of elements on the table.
(D) None of the above. This answer is incorrect.
Conclusion
The table is arranged so that each element is placed in one of the eight categories based on its chemical properties. Some elements are relatively abundant, while others exist only in trace amounts or were first discovered more recently. Each element is identified by its atomic number and symbol; the atomic number is represented using a group label, and the element’s symbol represents the name of the element.



